Simulation Center | About & Resources
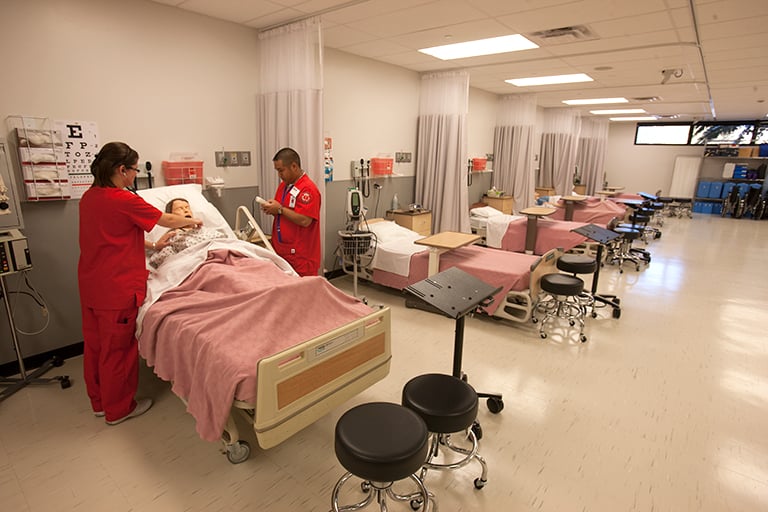
A Simulation Center is a dedicated area within a healthcare education building, medical center, hospital or training facility which is devoted to healthcare simulation. Healthcare organizations simulate clinical care activities at healthcare simulation centers which may include some or all of the following: use of life like and high fidelity manikins with varying levels of complexity (human patient simulation), virtual reality computerized animations, virtual simulations, specialized trainers for repeated practice of medical interventions (task trainers) and actors trained to behave and respond as patients (standardized patients). Across the world these immersive educational facilities are often called Simulation Centres.
All healthcare simulation educational methodologies are designed to instruct doctors, nurses and other healthcare practitioners through a process of immersive learning in which the learners respond to various patient clinical conditions and then reflect upon their own responses of clinical care to make changes as needed (debriefing). Nursing simulation, Surgical Simulation, and Healthcare simulation have become widespread in the healthcare field and hence the huge increase in the number of Simulation Centers across the globe.
Simulation Centers can vary in size but are dependent on the educational goals of the particular institution that houses the simulation center and the budget for the construction, operation and staff levels of the simulation center. Typically, a simulation center will have a clinical simulation scenario room which includes at least one patient manikin, an observation room which may be remote but where learners not involved in the healthcare simulation can observe the scenario and a debrief room where the clinical simulation activities are discussed after the scenario.
Sponsored Content:
In many medical simulation training centers, the observation room serves as the debriefing room. In addition, there is usually a separate control room where the simulation technician sits. This staff member is sometimes also dubbed a Simulation Technology Specialist who remotely controls the patient manikin, such as the Laerdal SimMan3G. The healthcare simulation technician is also responsible for set up the clinical simulation equipment and applying any special effects medical makeup called Moulage.
In addition, a clinical simulation educator will be present in the control room. The clinical simulation educator, who often speaks the voice of the patient manikin controls the physiological and spoken responses of the patient manikin. This usually is in response to the clinical interventions of the learners within the healthcare simulation lab. The above set up would be typical for a small healthcare simulation center.
HealthySimulation.com is dedicated to providing the latest Simulation Center news and healthcare simulation resources from around the world. To follow along, sign up for our free medical simulation email newsletter, follow @HealthySim on Twitter and @HealthySim on Facebook, or join our HealthySimulation.com LinkedIn Company Page!
Sponsored Content:
Now imagine a large-scale healthcare simulation center with multiple clinical sim labs, control rooms and debrief spaces. Add in patient clinical examination rooms with standardized patients, rooms full of task trainers, banks of computers and conference facilities and the simulation center could easily occupy thousands of square feet. These simulation centers cost millions of dollars to build and operate and are only found in larger medical centers and universities. Funding for simulation centers comes from donations, grants and university/medical center funding. Some simulation centers generate funds by renting out their spaces to other institutions or offering courses for which they charge a fee.
To build a simulation center, this involves a huge amount of planning. All the stakeholders come together and have input into the construction. The technical logistics and equipment required are complex. Some simulation centers have clinical simulation laboratories that exactly mimic an operating room, a delivery room, an emergency department, a medical surgical floor room, an ICU room etc. Experts from medical specialties and clinical simulation educators need to have input into the planning phase of the construction. Once the construction is complete, funds will be needed for ongoing maintenance, repair and replacement of healthcare simulation equipment as it ages and requires replacement.
View the LEARN CE/CME Platform Webinar Important Considerations When Designing a New Simulation Center to learn more!
In addition, qualified staff will be needed to provide the healthcare simulation based education program and schedule. Clinical simulation technicians are necessary to operate and maintain the complex equipment and clinical simulation educators are needed to run and debrief the healthcare simulation scenarios and courses. Staff are required to train and manage programs for medical students and advanced practice nurses that use Standardized Patients.
Technical staff at a Simulation Center will manage A/V Systems, Virtual Reality computers, surgical simulators and various other technology-based systems. In a few simulation centers, new medical products like those from CAE Healthcare or Gaumard are tested. There is the ability to practice new surgeries and new protocols for medical procedures are able to be developed in the simulation center environment. These rather specialized activities add another layer of complexity and also opportunity for innovation to simulation centers.
Click Here to Connect to Leading Healthcare Simulation Vendors!
Simulation centers have the ability to generate revenue for the organization which is housed in through a variety of measures such as to run healthcare simulation related courses of all levels in which the clinical simulation participant pays to attend. Simulation Centers can also potentially be an environment to be hired either internally or externally for research to be undertaken in a clinical simulated space. Simulation centers are also more and more being used by product development and innovation companies to hire and test new products prior to trial on actual patients in clinical care.
A simulation center can be a popular choice for people to want to sponsor and donate money to from a hospital or university based foundation. Many bequests are left by family members to want to continue to educate healthcare professionals. As healthcare simulation is a hugely successful and also effective way to be able to train healthcare professionals with a tangible and hands on immersive experience, this can be popular for donors who want to provide funding for the education of healthcare professionals in future generations.
Simulation Centers provide opportunities for healthcare practitioners and students at every level to develop their clinical skills and judgment. Accreditation is possible from groups like SSiH, ASPiH, and SESAM to name a few which you can learn more about by attendance at healthcare simulation conferences. Ultimately this leads to better patient outcomes and safer medical interventions through delivery of high quality healthcare simulation based education.
Medical Simulation Center Latest News

Dr. Pam Jeffries Upcoming Webinar on Developing Healthcare Simulation Centers to Create Realistic Clinical Scenarios!
How to Run a Clinical Simulation Program Without a Simulation Center

Healthcare Simulation Sustainability: Reuse, Refill, Recycle, Request
Sim-Zones: Sistema de Organización para el Aprendizaje Basado en Simulación Clínica

How Automation is Advancing Quality Healthcare Simulation

New Clinical Simulation Center Updates | January 2022
How to Run a Postpartum Hemorrhage Nursing Simulation Scenario

Celebrating the Holiday Season Across Healthcare Simulation

New Clinical Simulation Center Updates | September 2022

How Simulation Centers Can Expand Use and Support Innovation

Healthcare Simulation Escape Room Tips & Tricks | Part 1

How To Establish Effective Familiarization Across Healthcare Simulation
Sponsored Content:














