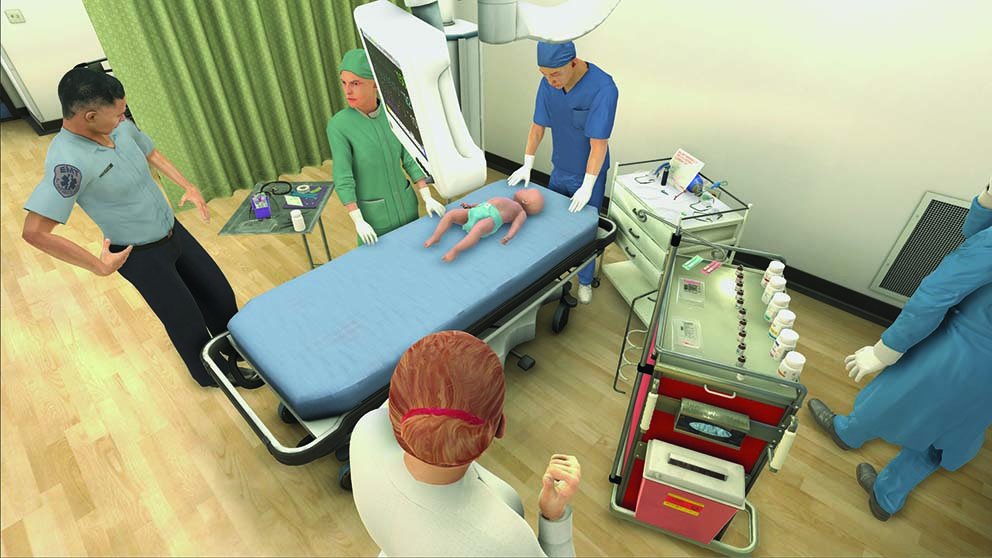
Virtual Reality in Medicine
Virtual Reality in Medicine is an emerging technology that can be used for both education and instruction within the healthcare field. Virtual Reality is used in Healthcare Simulation environments to allow learners to experience visual stimuli delivered via computer graphics, as well as other sensory experiences. A large benefit of advancing Virtual Reality in Medicine technology is that Virtual Reality lets students learn how to perform a number of tasks and procedures involving the human body without ever having to practice on a live patient.
How Virtual Reality in Medicine Simulates the Real Medical World
The most central aspect of Virtual Reality technology that makes it ideal for healthcare learners is its immersive capacity. When Virtual Reality is used in Clinical Simulation environments, it allows the simulated environment to surround a learner’s entire perceptual field. This means that the user feels psychologically present in the digital world rather than in their physical reality.
Sponsored Content:
Virtual Reality in Medicine is helping to train the next generation of healthcare professionals. Virtual Reality can be used to educate learners on diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, surgery, counseling techniques, and more. This Medical Simulation technology allows learners to practice their skills without fear of causing devastating errors. However, Virtual Reality does not rob students of the valuable lessons learned when interacting with real patients. Virtual Reality tools still provide the hands-on experience required to acquire familiarity with and comfort in performing procedures. As learners make mistakes, they can be thoroughly corrected in real time and without risk. Virtual Reality allows for ample practice so that skills can become second nature before they are applied in real-world scenarios. This makes Virtual Reality a safe and controlled setting for learners and their future patients, too.
Practical Examples of Virtual Reality Applications
From a first responder standpoint, Virtual Reality in Medicine can be used for paramedic training by having learners interact within simulated emergency scenarios. Virtual Reality can increase the realism of these high-pressure situations, which can enrich the learning experience. By learning to respond within the same environment as real-world situations, paramedic learners are better equipped to handle similar stressful situations in the field.
From a primary care standpoint, Virtual Reality can be used to help learners perfect their preventative medicine and counseling skills. Virtual Reality can teach learners how to assess patient conditions and provide insightful feedback and tips in real-time. Trainees can practice interacting with and educating patients on healthy practices through simulated Virtual Reality experiences. This can help trainees better determine how to assist their patients in making lifestyle changes, such as stopping smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, eating healthier foods, and pursuing daily exercise.
Sponsored Content:
Another way in which Virtual Reality in Medicine can assist learners is by teaching them the valuable skill of empathy. Empathy is demanded in situations across the healthcare spectrum, as providers are called upon to deliver bad news or manage particularly sensitive patient interactions. Practicing these conversations using Virtual Reality—and internalizing possible responses and reactions—can help learners prepare for the very real interactions that will arise within their intended practices.
HealthySimulation.com is dedicated to providing the latest VR in Medicine news and resources from around the world. To follow along, sign up for our free medical simulation email newsletter, follow @HealthySim on Twitter and @HealthySim on Facebook, or join our HealthySim LinkedIn Group!
Real-World Uses of Virtual Reality in Healthcare Education
The integration of Virtual Reality in Medicine has completely transformed the way healthcare is taught across colleges, universities, technical schools, and medical facilities. This method of learning is much more advanced and effective compared to the traditional combination of classroom experiences and textbook instruction.
At the university level, the faculty at Stanford University’s School of Medicine began using Virtual Reality for training within the school’s Neurosurgical Simulation and Virtual Reality Center in 2016. Within the center, a platform called Surgical Theater fuses several types of brain scans from actual patients so that neurosurgeons can more intimately understand a given patient’s anatomy. Scientists fuse 2-D images from MRI and CT scans using advanced computer programs to create 3-D images of a patient’s anatomy. Then, surgeons wearing Virtual Reality headsets can “fly” through the 3-D images and analyze a patient’s brain tissue and vessels without actually opening up their skull, according to the university.
Click Here to Connect to Leading Healthcare Simulation VR Vendors
Within Stanford’s Virtual Reality Research Center, 3-D printing is also used to help trainees better understand patients’ spine injuries, tumors, deformities, cerebrovascular disorders, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations. The ultimate goal of Stanford’s integration of Virtual Reality and Medicine is to improve surgical techniques and outcomes through mastery of surgical neuroanatomy and to enhance understanding of endoscopic skull base anatomy, microsurgical neuroanatomy, white matter dissection, and imaging.
Stanford also uses Virtual Reality to help medical students familiarize themselves with anatomic structures before their live instruction in the anatomy lab. The virtual reality warmup prepares students for in-person cadaver dissection, which comes next. Virtual Reality is also being harnessed to teach students in far-flung places throughout the world, such as in the case of Stanford’s 2020 initiative to teach anatomy to medical students in Kenya.
Several Companies Currently Offer Virtual Reality Products
Many companies have recently brought Virtual Reality products to market that can enhance the learning experience for healthcare professionals—below are several examples.
SimX: Seeking to push simulation forward, SimX developed a software system that was the first comprehensive professional-grade VR medical simulation system product available on the market. Founded in 2013 and headquartered in Mountain View, California, the platform allows medical teams to replace expensive manikins with incredibly flexible simulated patients, backed by a robust case creation engine.
PCS Spark: PCS Spark offers AI-driven virtual patient encounters for learners of all healthcare disciplines. These are the only virtual patients that can speak for themselves. Each PCS Spark scenario is a complete virtual persona with personal concerns, health history, and everything else you would expect to discuss during a clinical interview. All diverse and expansive patient scenarios are also crafted by PCS’s team of physicians, industry experts, and former standardized patient educators.
VRPatients: VRPatients is a physiologically-based Virtual Reality Simulation training platform that immerses a healthcare provider or first responder into actual case scenarios. Headquartered in Wilmington, Ohio, the VRPatients Healthcare Simulation training platform allows learners to interview, assess, diagnose and treat patients in real time. This technology offers many advantages, such as an enriched, sensory experience that leads to improved knowledge retention.
Oxford Medical Simulation: Oxford Medical Simulation (OMS) is a virtual reality platform that delivers quality, evidence-based, and highly realistic simulation. The platform, headquartered in Boston, Mass., assists in efficiently and effectively training healthcare professionals in world-class patient management practices to improve patient care, without the possibility of risking real human lives.
PrecisionOS: Precision OS is an innovative orthopedic virtual reality in simulation software company headquartered in Vancouver, British Columbia. The healthcare simulation company combines orthopedic surgeons with high-end game developers who work together to enhance the expertise of surgical simulation training worldwide.
Involve XR: Involve XR from Lumeto is an open and flexible learning & assessment platform for institutions looking to deploy data-driven, enterprise-grade, immersive training and assessment across healthcare and public safety sectors.
Virtual Medical Coaching: Virtual Medical Coaching’s Virtual Reality operating theatre radiation safety simulation allows operating theater workers to experience and learn how to keep themselves and others safe from ionizing radiation.
Osso VR: The company Osso VR provides a platform, content, and tools to bridge the surgical training gap. This Virtual Reality technology was created with the goal of increasing the adoption of higher-value medical technologies and democratizing global access to the latest surgical techniques. The platform is sold with a support program and advanced performance analytics with user-specific dashboards. These additions allow for objective assessment and review of technical skill data to give proficiency insight and maximize patient outcomes.
Fundamental Surgery: Fundamental Surgery, provided by FundamentalVR, offers a software platform that takes advantage of readily-available virtual reality software combined with cutting-edge haptics (the field involving the sense of touch). This creates a Simulation system that can be used on any modern PC setup, including a laptop. This learning tool requires a low hardware investment and a simple ongoing license fee.
MedVR Ed: The COVID-19 pandemic was a setback for healthcare professionals looking to get hands-on training experience. The lack of access to healthcare training centers, combined with a healthcare worker shortage, means that a shortage of 18 million healthcare workers could exist by 2030. The company MedVR Ed aims to address this issue by offering learners the opportunity to perform and practice their clinical procedural skills in a virtual environment. This solution is risk-free and enables countless practice sessions to help boost the confidence of learners. The MedVR Ed system offers in-depth data analytics on user competencies that help pinpoint the key areas that need improvement.
Ubi Sim: A final example of current Virtual Reality in Medicine offerings is the company UbiSim, which was recently acquired by Labster. UbiSim is a multidisciplinary Healthcare Simulation company working to combine Nursing Simulation and Virtual Reality for an immersive learning experience. Headquartered in Montreal, Canada, the company’s goal is to make Nursing Simulation more affordable, more accessible, and more realistic than ever. UbiSim offers a complete simulation lab on a flexible platform. This allows users to create and experience realistic clinical situations without needing to access physical Simulation Centers that are often booked months ahead of time.
PeriopSim: PeriopSim is an iPad and virtual reality experience-based simulation training solution for clinical educators in the operating room. The solution was created by Conquer Mobile and is now owned and operated by Conquer Experience, a healthcare simulation computer software company that specializes in training OR teams when experience is in short supply. The concept for PeriopSim draws from many years of experience in surgery simulation research and product development. The solution was developed in close collaboration with surgeons, nurses, healthcare simulation educators, and neuroscientists to ensure accuracy and realistic learning outcomes.
References:
Educators will use virtual reality to teach anatomy: https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2020/10/educators-will-use-virtual-reality-to-teach-anatomy.html
VR Medical Latest News

How to Leverage the Technology Acceptance Model to Enhance Healthcare Simulation Adoption

Most Watched Virtual Healthcare Simulation Webinars 2024

Global Medical Simulation Industry News Update June 2024

Transform Nurse Training: See Your Sim Space in New Ways with HTC VIVE XR Elite

Enhancing Nurse Competency: The Power of Virtual Reality in Interprofessional Education

Oxford Medical Simulation Platform Supports Debriefing VR Scenarios

Global Medical Simulation News Update May 2024

Varjo Mixed Reality Headsets Advance Aeromedical and Military Training

SimX VR: A Cost-Effective Revolution in Medical Simulation Training

Virtu-Wil Free Canadian Student Virtual Healthcare Simulation Program

HTC VIVE Survey Results of Current Role of XR in Healthcare
VR Scenario Building Made Easy with an Intuitive Authoring Platform: OMS Create
Sponsored Content: