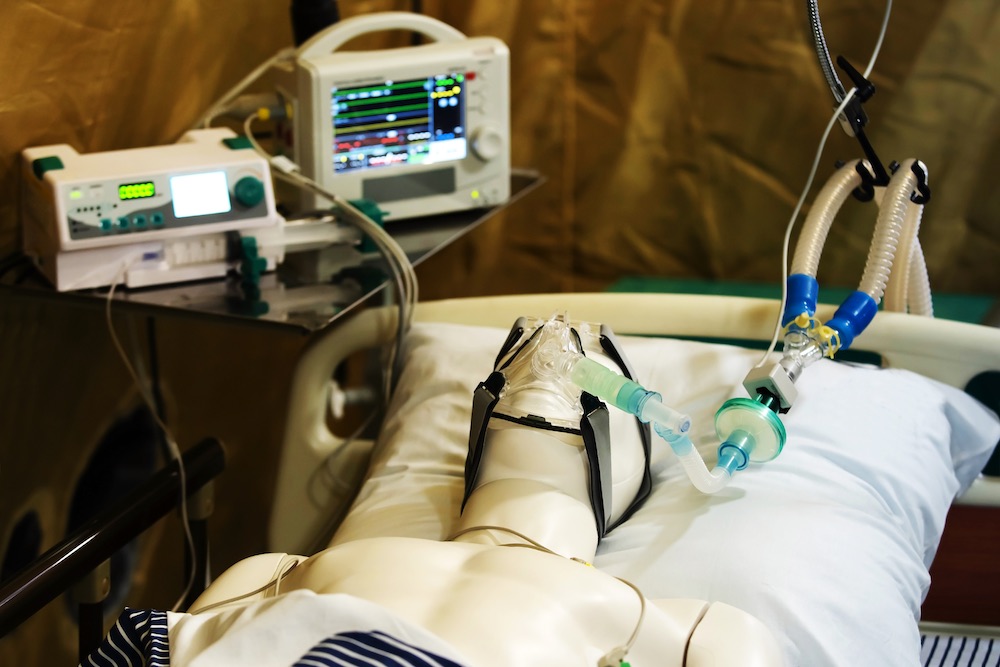
Defense Health Agency’s MST PMO Works to Optimize Warfighter Readiness and Improve Healthcare with Simulation
While the use of healthcare simulation is often associated with clinical simulation centers, hospitals, and academic institutions, the United States government recognizes the importance of medical simulation as well. Specifically, the Medical Simulation and Training Program Management Office (MST PMO) enables the Defense Health Agency (DHA), military departments, and Combatant Commands to rapidly prototype and field medical training capabilities to military hospitals and across the range of military healthcare operations. This is in support of an integrated medical readiness posture throughout the Military Health System (MHS). This HealthySimulation.com article shares more about these initiatives and their importance.
Co-located in the Central Florida Research Park with other core Team Orlando members, MST PMO was established by the DHA in 2016. Headed by Jude Tomasello, the office collaborates with the government and industry to provide quick and efficient delivery of solutions and capabilities that benefit the military health system.
Tomasello explained that the first 29 years of his career were spent in support of what he would call DoD’s “move, shoot, communicate” training aids, devices, simulations, and simulators. In 2017, he was asked to support a new Program Manager’s Office for Medical Modeling and Simulation. He recalls this as being a radical change from his experience, but that he was able to quickly and easily embrace the medical simulation and training community.
Sponsored Content:
“Whether on the battlefield or in a hospital, the level of dedication and commitment demonstrated by these providers was incredibly inspiring,” Tomasello explained. “Healthcare (or medical) simulation enhances training realism, which improves and sustains Readiness, which ‘saves lives and improves outcomes’ for our Nation’s men and women in uniform.”
He added the MST PMO was created to be the Acquisition Life Cycle Manager responsible for the development, acquisition, production, testing, fielding, and sustainment of medical simulation products and services supporting the Military Health System. Having a Program Manager performing and overseeing these activities provides the following benefits:
- The transition of medical training science and technology projects
- Support – the shared Services’ medical training requirements including geographic combatant commands requirements
- Standardization of medical training solutions
- Centralization of the sustainment of medical training solutions
This process ensures the MST PMO is able to provide the Military Health System (MHS) users the capabilities they need while being good stewards of U.S. taxpayer dollars. Tomasello recognizes that the future of healthcare simulation, like most other simulation fields, is firmly focused on Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality. He believes usage will increase as these technologies continue to advance, as further advancements in tactile realism are needed to be sufficient for healthcare providers, whether on the battlefield or in the hospitals.
“Manikin technology is advancing as well, albeit largely driven by the commercial markets. We expect to see manikins be able to more closely replicate human physiology and performance while being more durable, lifelike, and sustainable,” he said.
Sponsored Content:
Tomasello notes that this would allow more effective manikin product lines and would facilitate realistic en-route care using a single manikin from Role 1 Point of Injury to Role 4 Military Treatment Facility transitions and treatments. He also believes that advancements in healthcare simulation realism will allow for the Congressionally mandated reduction of live tissue training.
More About MST PMO
The MST PMO is committed to developing, acquiring, delivering, and sustaining medical simulation capabilities that optimize Warfighter readiness and improve healthcare. To meet this commitment, the Office uses training devices and systems, learning architecture, and on-demand training content to provide a number of services. These services include strategic sourcing, technology demonstrations and assessments, technology transition, and acquisition.
According to Team Orlando News, The Department of Defense (DOD) highlighted medical simulation training as a priority investment in its Military Health System (MHS) modernization and readiness description after medical simulation training was advanced as a top priority in the President’s 2021 Budget.
The news source added that the MHS investment strategy focused on “the transition of the military treatment facilities from the services’ Surgeons General to the Defense Health Agency and continued investments in trauma courses, medical simulation training, and electronic health records.” Team Orlando News explained that this noteworthy emphasis represents the “significance DOD holds in medical simulation and its considerable future in support of medical readiness and education.”
Tomasello explained that the office’s goals center around doing all that can be done to ensure DHA provides and sustains a Ready Medical Force. The MST office supports both Clinical and Operational training and readiness needs. In the near term, he says the Office plans to develop field simulations like the Complicated Obstetrics Emergency Simulation System (COES2) that greatly reduces life-threatening risks to mothers and newborns.
“We are also developing the Virtual Education Center (VEC), which is a portal designed to increase patient access and education as well as enhance Patient/Provider experiences,” he shared. “On the Operational side, we are continuing to support the SOCOM Purposed Emergency Access Response Point Of Injury and Trauma Simulation (SPEARPOINTS), which is in use training 18D Special Forces medics on a number of collective and prolonged casualty care tasks.”
Longer term, Tomasello says the Office intends to support the generation of requirements for the MTF Simulation Enterprise (MSE) (standardized, economical, and better learner outcomes), as well as Joint Operational Requirements that will be articulated in the Joint Point of Injury Training Systems (JPOINTS) Capability Needs Statement. Both the MSE and JPOINTS represent the future of medical simulation across the MTFs, the Services, and the Combatant Commands.
More About Military Healthcare Simulation
Military healthcare simulation is a type of clinical simulation that uses education and training principles to help members of the military and related professionals gain the skills needed in the field. Often, this guidance comes in the form of military simulation training, which can be accomplished in a number of ways. From the use of virtual reality simulation headsets to manikins and standardized patients, military simulations create realistic scenarios that military personnel must be ready and prepared for. These scenarios cover a wide range of experiences and focus relating to armed forces-based knowledge.
For example, today medics across the military are being instructed to use VR simulation training. These medical simulation experiences help provide them with a foundation of knowledge they can later rely on when engaged in real-life situations. By putting on lightweight virtual reality headsets, they are able to transport themselves into high-definition immersive simulation experiences. In these virtual spaces, military medics or learners can partake in a scenario to become better prepared for real-life situations. Further, each scenario can be customized to establish the most impact for the particular method or technique they are being trained on.
Another benefit of enhanced, hands-on healthcare simulation training is that this resource introduces learners not only to performance techniques but can mimic realistic battlefield and overseas conditions. While learning how to effectively treat hemorrhage, airway compromise, and tension pneumothorax is important, so is being able to provide aid in high-intensity situations in unfamiliar environments. With virtual reality simulation, this type of training is possible.
Learn More About the Defense Health Agency
Lance Baily, BA, EMT-B, is the Founder / CEO of HealthySimulation.com, which he started in 2010 while serving as the Director of the Nevada System of Higher Education’s Clinical Simulation Center of Las Vegas. Lance also founded SimGHOSTS.org, the world’s only non-profit organization dedicated to supporting professionals operating healthcare simulation technologies. His co-edited Book: “Comprehensive Healthcare Simulation: Operations, Technology, and Innovative Practice” is cited as a key source for professional certification in the industry. Lance’s background also includes serving as a Simulation Technology Specialist for the LA Community College District, EMS fire fighting, Hollywood movie production, rescue diving, and global travel. He and his wife live with their two brilliant daughters and one crazy dachshund in Las Vegas, Nevada.
Sponsored Content: