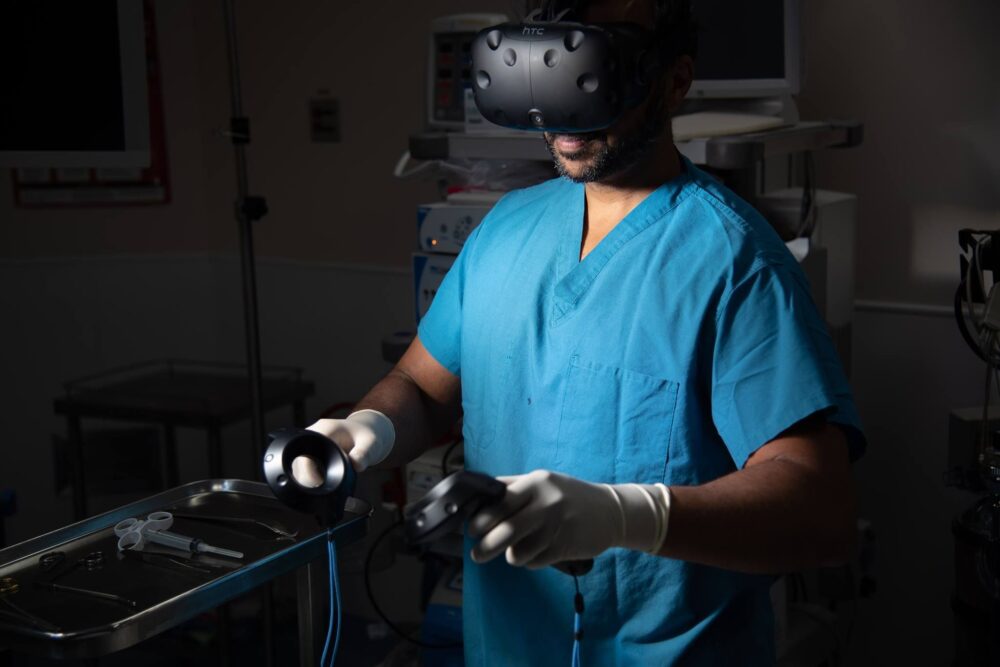
HTC VIVE: How Healthcare Training is Becoming More Accessible with XR
Extended Reality (XR) hardware provider HTC VIVE has recently collaborated with HealthySimulation.com to create several key resources for healthcare professionals considering the use of XR in clinical education and training. By sharing open-access resources covering strategies to unlock use cases, VIVE and Healthysimulation.com demonstrate how XR technology is changing the face of clinical education and training. Click to download the Designing XR Training Solutions for Healthcare ebook today!
As educators begin adopting XR for healthcare education curriculum and on-the-job training, analysts expect the demand for healthcare-related XR training solutions to grow by nearly 37% by 2028. But before medical professionals commit to an investment, they are first asking themselves how XR can practically improve their operations. Most healthcare organizations go in with a goal such as decreasing operating costs, lowering capital expenses or increasing learning outcomes as the “North Star” to tracking the effects of their investment. For this article specifically, HealthySimulation.com will explore one component to the benefit of XR, being the accessibility of learning outcomes while diving into a few specific XR applications in the market today.
https://youtu.be/x3MfiWkDfqo?feature=shared&vq=hd1080
Sponsored Content:
The Benefits of XR Medical Simulation
Throughout the century there have been numerous studies on the effects of kinesthetic learning and its effects on knowledge retention Which has led to the rise of physical simulators such as manikins. However, there are drawbacks that prove solutions such as manikins to be inflexible and costly. Most notably, accessibility has come into question. When there is one manikin for a class of 20 students or a classroom of online learners, how do each student ensure they receive the desired practice time to become sufficient in one, or even dozens of procedures. This is where XR enters the conversation. Pioneers such as Jack Pottle, co-founder and chief medical officer of Oxford Medical Simulation, reports numerous impacts virtual reality has in healthcare education such as the potential for numerous learners to engage in genuinely interprofessional, highly realistic simulations without being constrained by geography. Many others back-up this claim such as one 2022 PwC survey that shows how many companies are beginning to start or accelerate VR learning for VR-based upskilling and collaboration. The following are addressed in this report:
- Increased accessibility with remote access that does not require a physical medical simulation facility.
- The repeatability of VR scenarios without the time wasted on physical simulations
- The cost of time to replenish disposable gear or other implements.
- Technical and soft skills, such as leadership and resilience that are repeatable in an XR scenario
View the LEARN CE/CME Platform Webinar Transform Medical Simulation Education Curriculum with Generative AI and VR to learn more!
Featured XR Applications on the Market
Sponsored Content:
Through the rise of XR in healthcare, VR hardware manufacturers such as HTC VIVE have invested heavily in training solutions to improve training and patient care outcomes. These investments have led to advancements in training healthcare providers to improve access and quality of care. A few of these companies will be reviewed below to demonstrate a wide variety of applications.
Virti – A No-Code Solution to Improve Patient Safety and Reduction of Healthcare Provider Burnout
HTC VIVE and Virti have partnered to assist healthcare professionals to develop XR material for clinical simulations that can be updated in-real-time. Developing XR cases can be “the most challenging part because in the past you needed an engineer and a designer to do it, and that’s expensive,” says Lewis Chang, head of the HTC VIVE Medical VR team in Taiwan, and this “wasn’t feasible for most of our customers who are medical professionals.”
Virti is a “no code” technology for developing and conducting immersive training content. More importantly, Virit was designed with the medical profession in mind. “No code” refers to the user needing simple basic computer skills. Lewis says Virti is akin to “PowerPoint for VR.”
To prove ease of use for the medical community with Virti, the HTC VIVE Medical VR team conducted 85 workshops in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region. In those workshops, 2,500 medical professionals and students, who in turn, have used Virti to create 183 different simulations to improve patient care through VR that includes Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), targeted temperature management; Da Vinci surgical training; Hospice care; and many others. This partnership addresses a gap identified in a cost-effective way of combining technology and medicine to improve the education of medical providers through XR.
Periopsim – A Game-Based VR Simulation Training and Assessment Platforms for Perioperative Educators.
Boston Children’s Hospital’s Cardiovascular Operating Room (CVOR) wanted to expand its capacity to train new surgical scrub personnel through simulation because of the expansion of the number of CVOR rooms. One issue was the training capacity was already at the limit due to space limitations within the CVOR in a patient case. So, a decision was made to explore VR solutions. After reviewing the adult modules in PeriopSim, the educators saw the value of the approach—scrub trainees could memorize instruments and learn procedures without burdening instructors, OR space, or equipment.
In a funded project, a multidisciplinary team collaborated to produce the first-ever series of pediatric heart surgery modules. Further modules have been developed: On/Off Bypass, Arterial Switch, Bidirectional Glenn, Cone Repair, Extracardiac Fenestrated Fontan, Stage One, Tetralogy of Fallot, and VSD.
The new pediatric modules have been incorporated into the training of nurses to the circulator and surgical scrub roles. A Tiered Skills Acquisition Model (TSAM) model ensures that every learner has learned each component skill before progressing to the next group of competencies. Learners practice with actual instruments, memorize their names through flashcards, take mini quizzes, observe surgeries, and participate in lectures/discussions.
The project has been a success. Circulator and surgical scrub trainees gain valuable skills in a quiet, self-directed study with the iPad and, later, the HTC VIVE headset. Moreover, VR allows them to practice certain spatial tactile reasoning and complete the work in a more realistic environment. This addressed the bottleneck concern for additional training in the CVOR, costs, and tiered learning with multiple checkpoints in the training process.
Why Healthcare Providers Choose VIVE?
In short, security. VIVE is manufactured in TAA-approved Taiwan, providing distinct advantages over competitors such as Meta and Pico, both of which are manufactured in China. TAA compliance is crucial for government-funded entities with stringent hardware procurement requirements. Additionally, VIVE’s compliance with 889 regulations prohibits federal contracts involving certain blacklisted telecommunication and video surveillance equipment, contributing to national security efforts.
In operational terms, VIVE is designed for enterprise use. It simplifies fleet management by allowing multiple headsets to be managed under a single account, significantly reducing administrative workload. Unlike Meta, VIVE doesn’t require additional subscriptions for share mode on each headset, resulting in cost savings. Additionally, VIVE prioritizes data privacy by minimizing data collection and restricting third-party access, which aligns seamlessly with healthcare regulations. These features make VIVE the top choice for healthcare VR initiatives, enhancing both patient care and security.
As healthcare educators and professionals explore the potential of XR technology for medical simulation and training, it’s clear that the demand for XR solutions in healthcare education is on the rise. With an expected 37% growth by 2028, the focus is shifting towards practical improvements in operations such as accessibility. The next segment article will explore how organizations are prioritizing XR to reduce costs and shore-up their bottom-line.
Teresa Gore, PhD, DNP, APRN, FNP-BC, CHSE-A, FSSH, FAAN – Dr. Gore has experience in educating future nurses in the undergraduate and graduate nursing programs. Dr. Gore has a PhD in Adult Education, a DNP as a family nurse practitioner, and a certificate in Simulation Education. Dr. Gore is an innovative, compassionate educator and an expert in the field of healthcare simulation. In 2007l Teresa started her journey in healthcare simulation. She is involved in INACSL and SSH. She is a Past-President of INACSL and is a Certified Healthcare Simulation Educator Advanced (CHSE-A). In 2018, she was inducted as a Fellow in the American Academy of Nursing (FAAN). In 2021, she was inducted as a Fellow in the Society of Simulation in Healthcare Academy (FSSH) and selected as a Visionary Leader University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Nursing Alumni. During her career, Dr. Gore has led in the development and integration of simulation into all undergraduate clinical courses and started an OSCE program for APRN students. Her research interests and scholarly work focus on simulation, online course development and faculty development. She has numerous invited presentations nationally and internationally on simulation topics.
Sponsored Content: