HelpMeSee’s Healthcare Simulation Training & Partnerships Deliver New Hope for Cataract Blind
Across healthcare simulation, the ability to innovate and adapt to ever-changing environments is critical. As the global pandemic continues to vastly impact the healthcare industry, the need to innovate clinical simulation-based training has become more critical than ever before. Now, this medical simulation training is being used to meet the challenges of some of the world’s growing public health challenges, including the 100 million people who make up the world’s cataract blind. Specifically, the organization HelpMeSee is using virtual-reality, simulation-based training to increase the number of cataract specialists who can perform surgery for the blind.
This transformational technology has applications in the developing world, where the world’s poor lack access to sight-restoring surgery. The global pandemic has also drastically decreased opportunities for ophthalmology residents to practice their surgical skills, a void that simulation-based training is now filling.
Another way healthcare simulation-based training has proven advantageous for ophthalmologists with decades of experience is through the ability to keep their skills fresh. This is important as, often, their time in live surgery has been limited due to delays in cataract surgeries from COVID-19.
Sponsored Content:
Simulation-Based Technology: From Aviation to the Cataract Blind
The HelpMeSee simulator was the vision of Al Ueltschi and his son, Jim. During his career, Ueltschi became the founder of FlightSafety International, the world’s preeminent aviation training organization and Co-Founder of Orbis International. Then, in 2010, Ueltschi and his son saw the opportunity to adapt the use of healthcare simulation-based technology that had been successfully utilized in commercial aviation. Their goal was to help the cataract blind, and thus they launched HelpMeSee. Recognizing the economic and human impacts of cataract blindness, their vision led to the use of clinical simulation-based training to educate more learners, more quickly, to fight this growing humanitarian crisis.
Transcending Borders and Overcoming Boundaries
Today, HelpMeSee is led by Saro Jahani, who left a career on Wall Street to join the global organization. He took the reins as President and CEO of the organization after having served as Head of Global Innovation and Technology. Jahani brings decades of experience in digital transformation and agile product development to the organization. In March of 2020, he and his team had a deadline of just months to complete the remaining 80% of the development of the eye surgery simulator, even as the future of the COVID-19 pandemic was unknown.
Sponsored Content:
Facing unforeseen global challenges, supply chain issues, and a need to improve lead time and drive high performance, Jahani led a team through a complex engineering and software design to complete the healthcare simulation process for the cataract procedure. Uniting a team of professionals across three continents, eight countries and multiple time zones, Jahani and his team thereby launched the world’s first virtual reality high fidelity MSICS simulator with an instructor-led curriculum in just a few months.
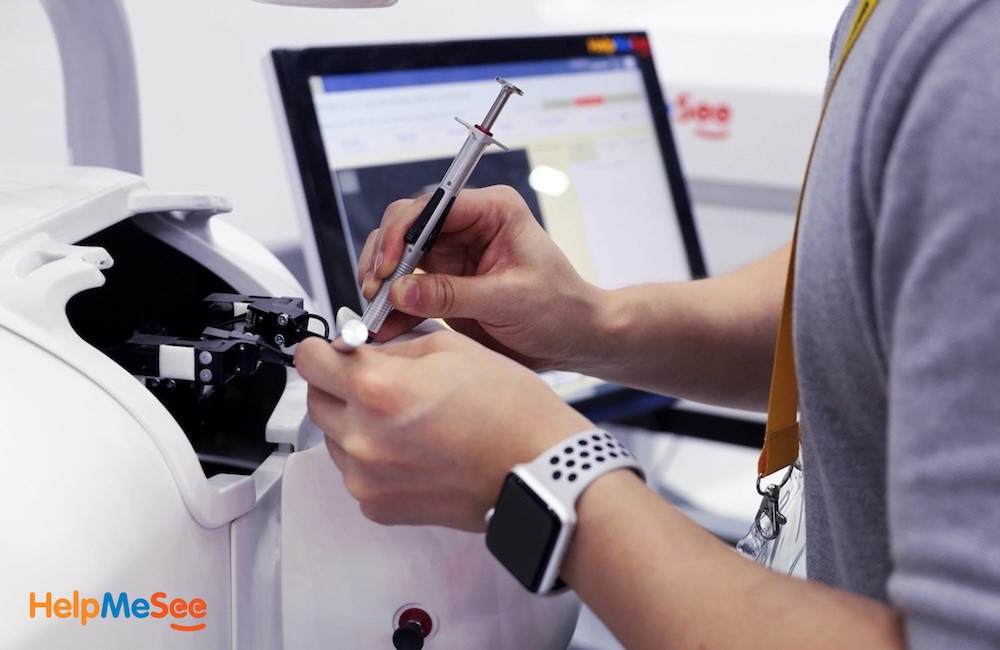
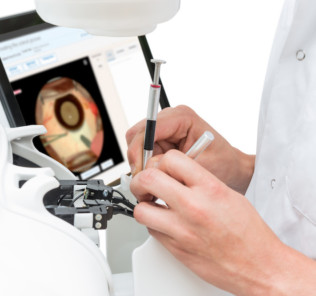
HelpMeSee Simulator and Courses
Specifically, HelpMeSee offers MSICS Simulation-Based Training Course (MSTC), which is a proficiency-based training course for cataract surgeons in Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery (MSICS). Drawing on virtual reality, HelpMeSee’s Simulation-Based Training program offers an authentic experience of live surgery, allowing for the scalable training of large numbers of cataract specialists, with unprecedented speed and skill.
Further, the training builds competency, reducing cataract surgery training time, with better outcomes than traditional surgery methods. Such training additionally allows cataract specialists to practice surgery and learn to address complications through simulation, rather than the human eye with a live patient.
“Individual customization of training is a significant advantage, as the data on surgical steps can be tracked on the system,” explained Jahani. “The simulation-based training and curriculum provide an authentic experience, allowing for errors without risks to patient safety.”
Innovation that Drives Change
Ultimately, the HelpMeSee team is using healthcare simulation-based training to drive change. To meet its mission, the organization has developed strong working relationships with governments, NGO’s, researchers, and leading universities around the world.
“Reaching the cataract blind requires an ecosystem of partnerships and scientific know-how, coupled with a commitment to a broader vision and genuine passion,” said Jahani. “Working with our partners around the world, we’re fighting against a public health crisis that threatens the quality of life for millions of people. Together, our work is grounded in the fact that for every 1,000 surgeons trained, 100,000 more cataract surgeries are possible each year.”
In many places around the world, access to care is dramatically limited and there is little hope for those who are blind due to cataracts. Using the power of simulation-based training, HelpMeSee and their partners are working to change that, as they restore sight and restore lives for people in great need.
Overall, HelpMeSee understands the complexity and large-scale change needed to reach marginalized populations but understands that the organization cannot achieve this mission alone. Therefore, HelpMeSee seeks to build a sustainable model with partners and place training centers in each of the poorest regions with the highest rates of vision loss to make the largest impact on this issue.
Learn More About HelpMeSee
Sponsored Content: