Healthcare Simulation Center Floor Plan Insights & Resources
Healthcare simulation centers greatly benefit facilities and institutions by providing opportunities for healthcare practitioners and learners at every level to develop their clinical skills and judgment. In providing clinical simulation resources and instruction, simulation centers are tasked with finding innovative ways to maximize their space and available resources. For this reason, healthcare simulation center leaders develop specific floor plans to ensure that the facility is as efficient and effective as possible. This article shares insights into the floor plans at a number of prominent simulation centers.
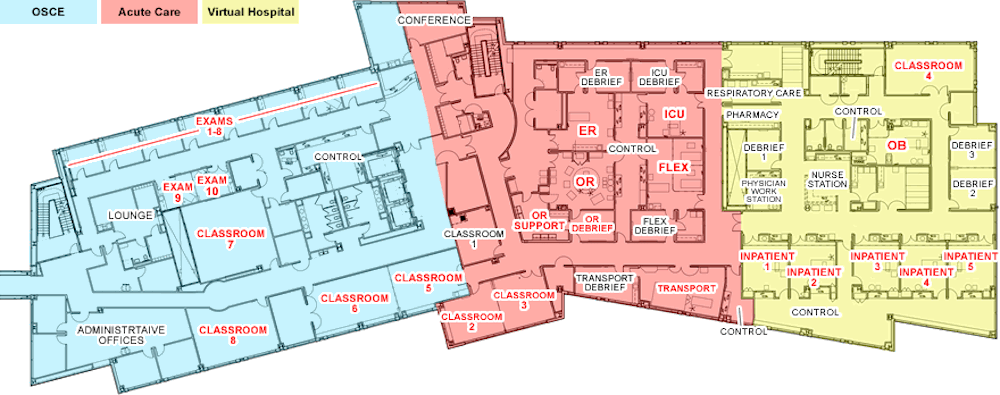
Indiana University Health Simulation Center: This university simulation center’s OSCE wing includes a number of classrooms, exam rooms, administrative offices, and a lounge. In terms of the acute care wing, there is an emergency room, operating room, intensive care unit, flex room, classrooms, transport room, and debriefing rooms. Within the virtual hospital, there is a nurse station, pharmacy, respiratory care room, inpatient rooms, and classrooms. These classrooms contain audio-video technology such as microphones for audio recording, a public address system speaker, cameras for video recording, a laptop PC workstation, a telephone, and a wall-mounted LCD display.
Sponsored Content:
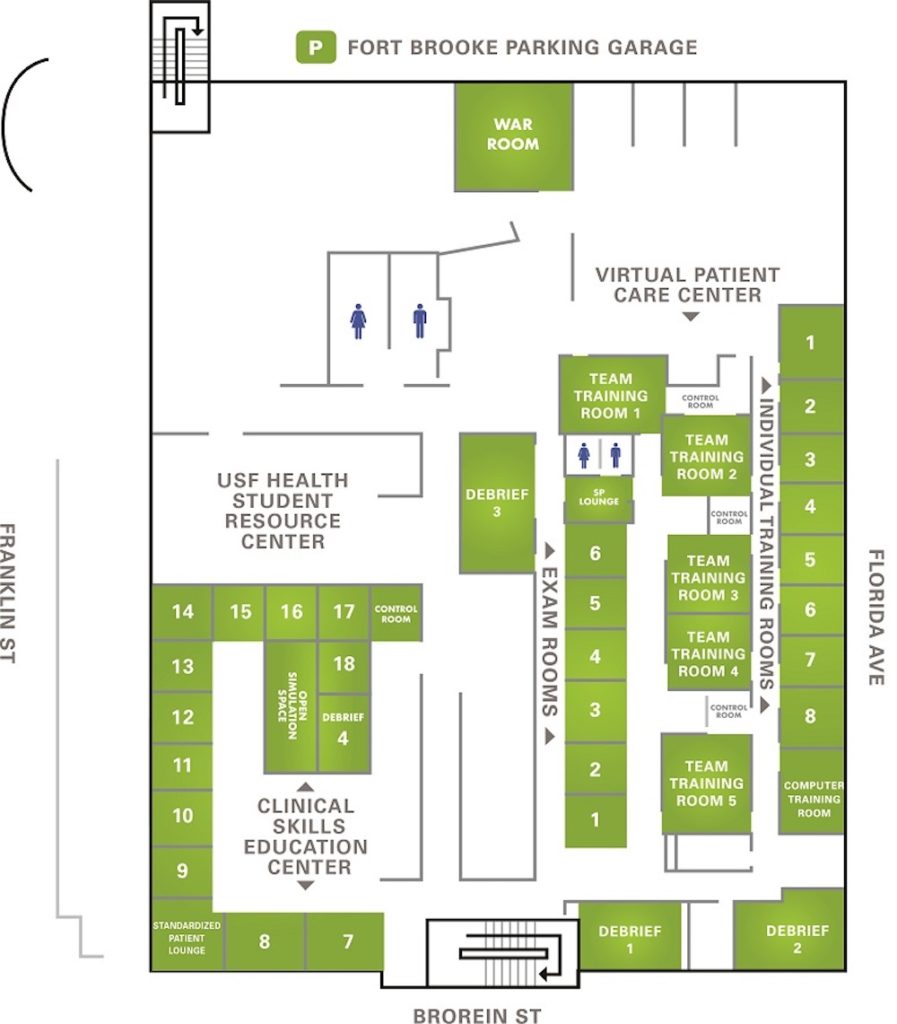
Center for Advanced Medical Learning and Simulation (CAMLS): This simulation center has three floors. The first floor is used for bio skills labs, the second as meeting and education space, and the third floor for simulation and clinical skills. Specifically, the third floor houses team training rooms, a debriefing room, an open simulation space, and several exam rooms. The CAMLS website shares information about each room name, area (sq ft), dimensions, classroom, theater, u-shape, and hollow square.
Penn Medicine Simulation Center: Clinical Simulation at Penn Medicine is 22,000 sq. feet located in what was previously an operational OR suite, PACU, pre-operative holding area, and endoscopy suite. This is located on the second floor of a facility that also houses long-term acute care, hospice, and rehabilitation services. The space has been renovated to include a control room (CORE), large conference room, multi-skills lab, individual “sim” rooms, task trainer rooms, a standardized “sim” patient exam area, faculty observation rooms, breakout rooms, an administrative suite area, and computer rooms.
Sponsored Content:
University of California, Irvine Medical Education Simulation Center: This simulation center contains a debriefing room with high-quality audiovisual equipment that can record and playback clinical simulations at will. Also within the center, a UCI Simulation Center hospital ward offers a full scope of acute and general care services including, cardiac, geriatric, pediatrics, and inpatient related management. Additionally, there is an operating room, control room, clinical skills area, ED/OB trauma bay, and intensive care unit.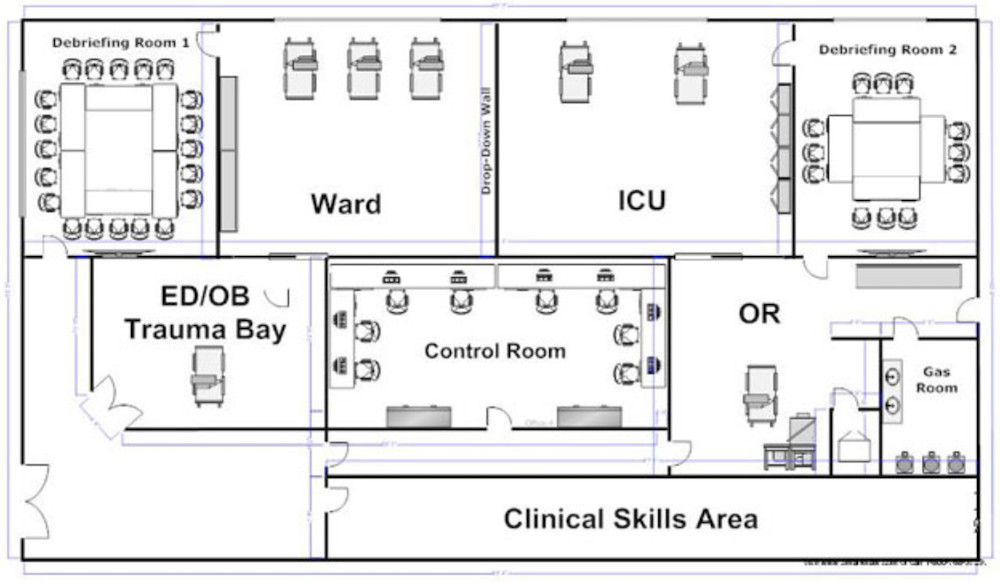
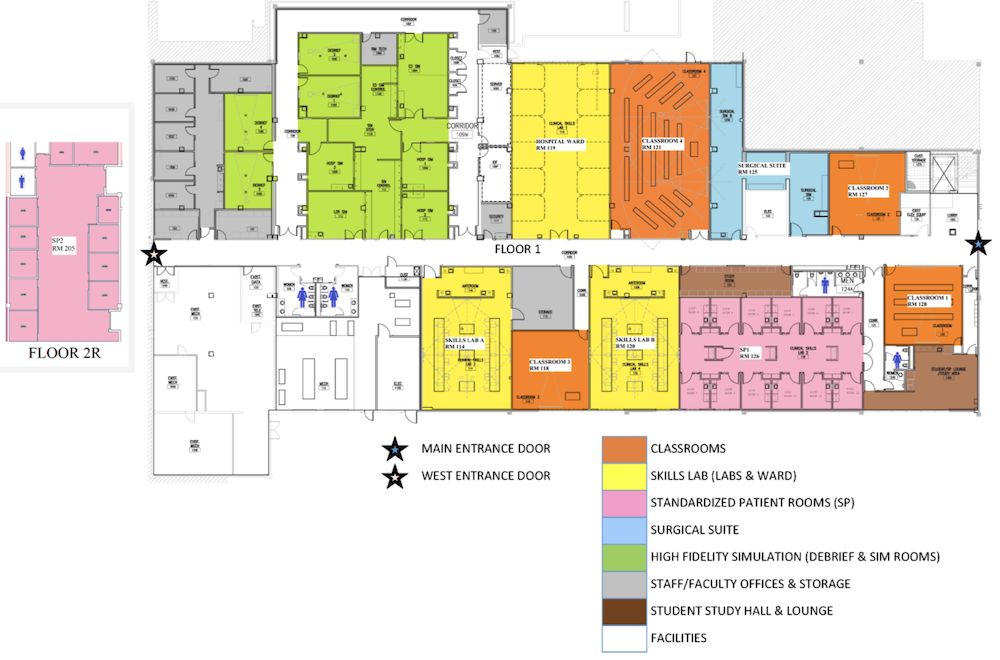
Clinical Simulation Center of Las Vegas: This simulation center has four classrooms and three skills lab rooms (labs and ward). There are also several standardized patient rooms, a surgical suite, and an area designated for high-fidelity simulation (including debriefing and simulation rooms). Staff and facility offices, as well as spaces for storage, exist throughout the simulation center. Further, there are two study halls and lounge areas.
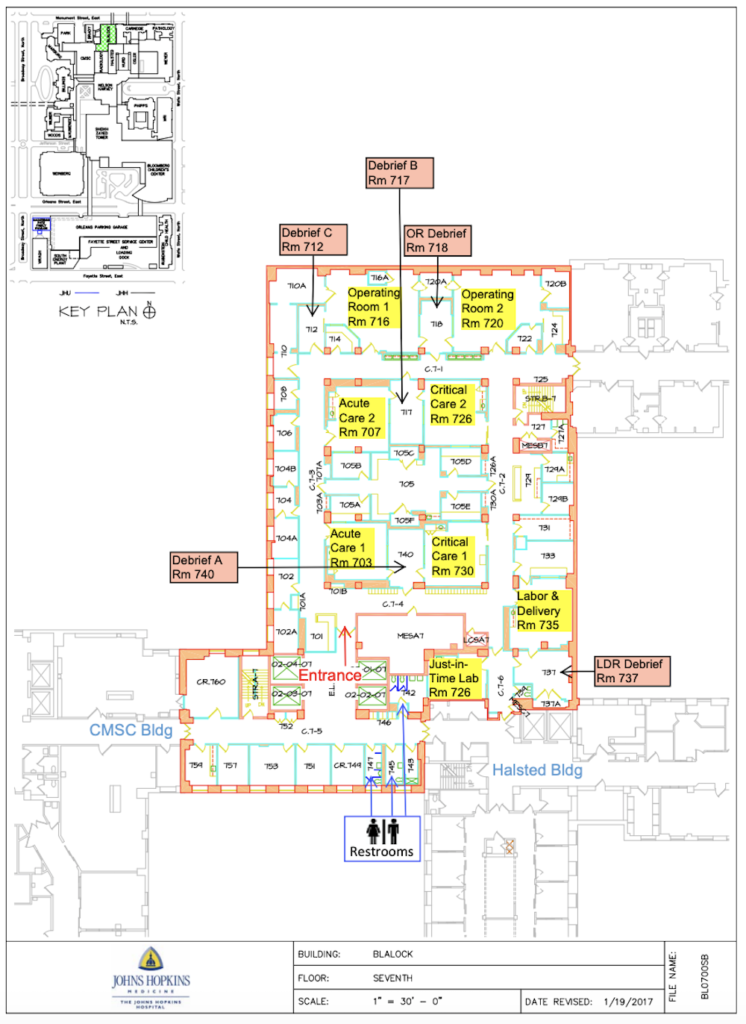
Johns Hopkins Medicine Simulation Center: The state-of-the-art facilities are currently shared between two locations, one on the seventh floor of the Blalock building, and the other on the top floor of the Johns Hopkins Outpatient Center. Opened in 2016, the Blalock Sim Hospitals features two acute care rooms, two critical care rooms, two full-size operating rooms, a 24-hour just-in-time training lab, and a labor and delivery suite. There is also a nurse’s station and advanced multimedia capabilities.
Opened in 2008, the John Hopkins Outpatient Center contains a 50-person conference room and an operating room simulation room with a one-way mirror and video monitoring. There are also two Intensive Care Unit simulation rooms with one-way mirrors and video monitoring, twelve exam rooms for standardized patient exams, and more video and monitoring capabilities.
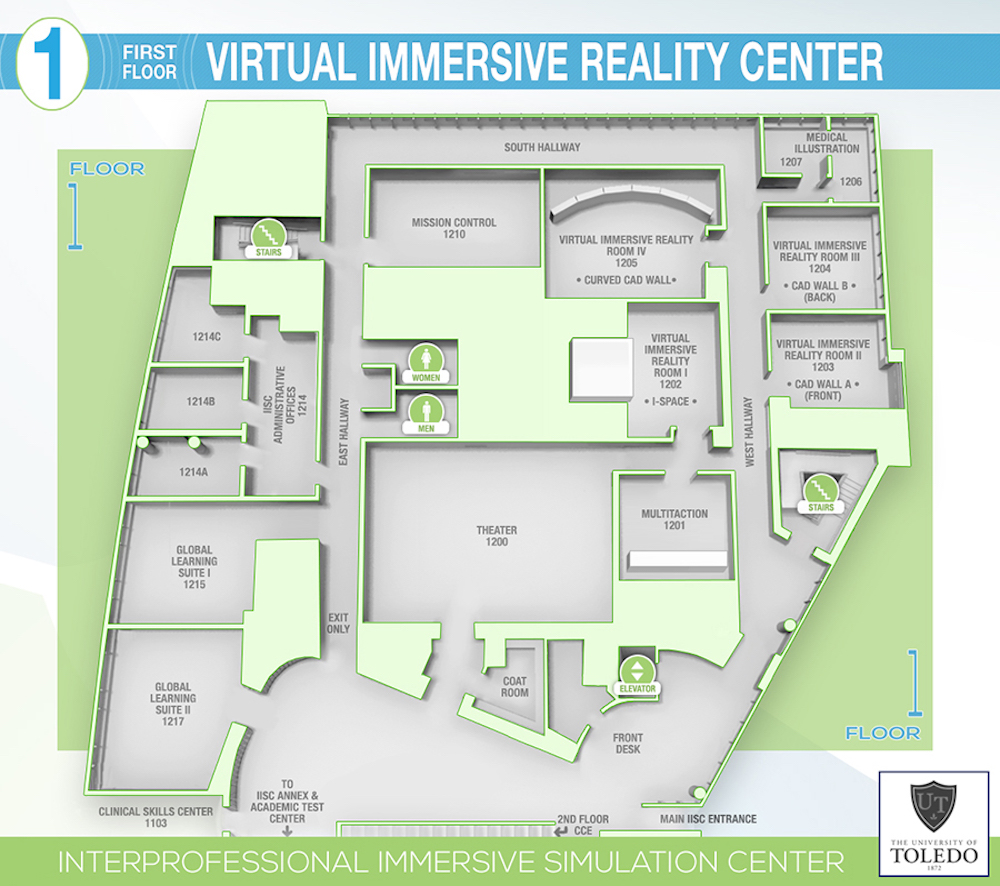
University of Toledo Interprofessional Immersive Simulation Center: The IISC is a three-story, 65,000-square-foot building located on the Health Science Campus. The center includes the introduction of 3D and Virtual Immersive Environments to medical education. A welcoming, highly technical lobby and displays, global learning suite, multi-purpose theater, virtual immersive spaces, and administrative and medical illustration offices are located on floor one. The main hub of IISC’s Advanced Surgical Skills Center and team members are on floor two.
The state-of-the-art elliptical hospital is a central control hub surrounded by four different simulation rooms. There are also breakout rooms and additional rooms equipped with simulation trainers and models. Surgical simulation training suites, fresh tissue labs, virtual operating suites, and The Merrick Surgical skills lab, named after one of IISC’s most supportive family and surgeons Dr. Hollis Merrick and Dr. Mary R. Smith, are all located on floor three. A Medical History Gallery for plastination models, historical medical equipment, and other items are also on display. Lastly, IISC’s home healthcare suite, the innovation labs, a collaboration, a technology development, and a 3D creation suite are all located on the lower level.
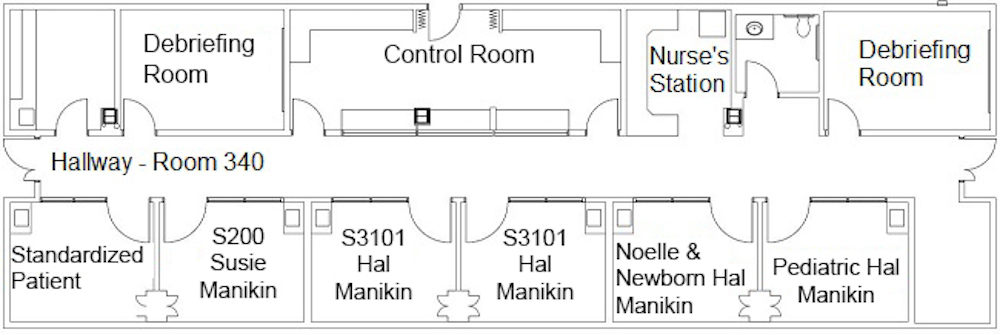
Boise State University Simulation Center: This simulation center utilizes six high fidelity manikins (adult, pediatric, and maternity/infant) and is fully interactive with real-time patient data (vital signs, cardiac monitoring, and respiratory status) equipment and displays at the bedside. The six-room simulation center has a central “nurse’s station” similar to those found in acute care institutions. The simulation center also houses simulation debriefing rooms, full audio-visual capabilities, and flat-screen monitors.
More About Simulation Centers
A Simulation Center is a dedicated area within a healthcare education building, medical center, or training facility which is devoted to medical simulation. Healthcare organizations simulate care activities at these centers which may include some or all of the following: use of life-like manikins with varying levels of complexity (human patient simulation), virtual reality computerized animations, specialized trainers for repeated practice of medical interventions (task trainers) and actors trained to behave and respond as patients (standardized patients). In Europe, these educational facilities are called Simulation Centres.
All of these educational methodologies are designed to instruct doctors, nurses, and other healthcare practitioners through a process of immersive learning in which the learners respond to various patient conditions and then reflect upon their own responses making changes as needed (debriefing). Nursing simulation, Surgical Simulation, and Healthcare simulation have become widespread in the healthcare field and hence the huge increase in the number of simulation centers.
Learn More About Simulation Centers
Lance Baily, BA, EMT-B, is the Founder & CEO of HealthySimulation.com, which he started while serving as the Director of the Nevada System of Higher Education’s Clinical Simulation Center of Las Vegas back in 2010. Lance is also the Founder and acting Advisor to the Board of SimGHOSTS.org, the world’s only non-profit organization dedicated to supporting professionals operating healthcare simulation technologies. His co-edited Book: “Comprehensive Healthcare Simulation: Operations, Technology, and Innovative Practice” is cited as a key source for professional certification in the industry. Lance’s background also includes serving as a Simulation Technology Specialist for the LA Community College District, EMS fire fighting, Hollywood movie production, rescue diving, and global travel. He and his wife Abigail Baily, PhD live in Las Vegas, Nevada with their two amazing daughters.
Sponsored Content: